■ Buffer Busy Wait
- 동일한 데이터 블록에 대한 액세스에서 발생한 대기.
- 특시, 같은 데이터 블록에서 서로 다른 행을 조회하거나 변경하는 동시성 상황에서 발생한다.
▶ 대기 상황
1. 조회 시 (Shared Mode)
- 한 세션이 데이터 블록을 shared mode 로 읽고 있는데, 다른 세션이 동일한 블록의 서로 다른 행을 배타적인 모드(exclusive mode)로 변경.
2. 변경 시(Exclusive Mode)
- 한 세션이 데이터 블록을 배타적인 모드(exclusive mode)로 변경 중인데, 다른 세션이 동일한 블록의 서로 다른 행을 읽거나 변경하려고 할 때 발생.
▶ 대응 방법
1. 트랜잭션 디자인 수정 : 서로 다른 행에 대한 액세스 충돌을 최소화하는 트랜잭션의 설계을 고려
2. 인덱스, 파티셔닝 등 활용 : 데이터 블록에 대한 경합을 줄이기 위해 인덱스나 파티셔닝 등을 활용하여 세션 간 충돌을 최소화.
3. 동시성 제어 : 서로 다른 세션 간의 동시성 제어하는 기법을 적용하여 Buffer Buy Wait event 를 방지한다.
- 각 사용자는 행을 변경하기 위해서는 tx lock(row level lock, 변경하려고 하는 행의 lock) 을 exclusive mode 로 획득했다고 하더라고 현재 자신만 블록안에 있는 행을 변경해야 하는 것을 보장받아야 한다.
이때 블록 헤더에 exclusive lock 을 설정 해야 한다. 이 lock은 block lock 개념이다.
#) (상황) A : 급여를 100 -> 200 으로 수정 / B : 급여를 200 삭제 => 이전 값은 undo 에 저장
▶ 작업순서
1. 변경하고자 하는 행의 해당하는 블록이 data buffer cache 에 있는지 실행계획을 통해서 찾아 간다.
-> Latch 을 잡고 찾아간다. (shared mode)
-> 만약 Latch 을 잡지 못했다면? latch : cache buffers chains
2. data buffer cache에 있는 블록을 찾아서 블록 헤더에 블록 lock(shared mode: select문 / exclusive mode: DML) 을 획득하게 되면 latch 해제된다.
3. select문 끝나면 : 원하는 행을 active set 결과를 만들면 block lock 해제
3-1. DML 작업이 끝나면 : tx lock을 획득하고, 원하는 행을 변경이 끝나면 block lock 해제
3-2. DML 작업이 끝나면 : tx lock 을 획득하지 못하면 대기(enq : TX - row lock contention) 하게 되면 block lock 해제 된다. waiting 단계에서 해제 되면 다시 block header에 exclusive mode을 획득하고 작업을 수행한다.
< HR_1 >
update hr.employees set salary = 1000 where employee_id = 100;
< HR_2 >
update hr.employees set salary = 2000 where employee_id = 100;
waiting..
<SYS session>
select sid, event from v$session where username = 'HR';
<HR_3>
=> enq: TX - row lock contention이 걸려 있는 사원 조회 해보기!
select * from hr.employees where employee_id = 100;
select * from hr.employees where employee_id = 110;실행 가능
=> block lock 해제
<HR_1>
update hr.employees set salary = 1000 where employee_id = 100;
rollback;
<HR_2>
update hr.employees set salary = 2000 where employee_id = 100;waiting.. → update 변경
<SYS session>
select sid, event from v$session where username = 'HR';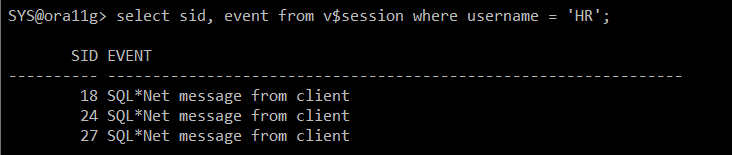
■ 물리적 I/O 발생
latch 를 잡고 hash bucket 에 블록에 해당하는 버퍼 헤더(DBA+block class)가 존재하지 않는다면 물리적인 I/O가 발생.
□ LRU(Least Recently Used) LIST
- buffer cache의 관리를 위해 사용되는 리스트로, buffer의 가장 최근 사용 여부에 따라 분류된다.
- 사용된 buffer, 미사용 buffer(free buffer), 변경된 buffer(dirty buffer) 등을 효율적으로 관리하는데 사용
1) 메인 list
- hot region(자주 사용된 영역) : 자주 사용되는 buffer들이 속하는 리스트로, 메모리에 오랫동안 보존될 것으로 예상.
- cold region(사용빈도수가 낮은 영역) : 사용 빈도가 낮은 buffer 들이 속하는 리스트로, 메모리에서 제거될 가능성이 높음.
2) 보조 list(먼저 본다)
- Free Buffer List(미사용 버퍼 리스트) : 아직 사용되지 않는 버퍼들의 리스트로, 새로운 데이터를 캐시하기 위한 자리를 마련하는 역할.
- DBWR(Database Write)에 의해 관리되며, 여러 이벤트(예: 체크포인트 발생) 에 의해 기록된 버퍼들이 속함.
참고사항)
checkpoint 발생 시점
1) drop 또는 truncate | 2) 정상적인 DB 종료 | 3) 로그 스위치 발생 | 4) alter system checkpoint; 명령어 수행
5) 병렬 처리 작업 수행 | 6) free buffer 를 찾지 못했을 경우 | 7) 특정 tablespace를 offline 또는 online 으로 변경할 때
8) 비정상적인 DB 종료 이후 복구
□ LRUW(Least Recently Used Write) LIST
- 아직 디스크로 기록되지 않은 변경된 buffer(dirty buffer)들을 관리하는 리스트
- dirty list, write list 라고도 한다.
1) 메인 리스트 : 변경된 buffer들의 리스트, 디스크에 기록되지 않은 상태.
2) 보조 리스트 : 현재 DBWR에 의해 기록중인 버퍼들의 리스트,
물리적(physical)인 I/O 발생하면 latch 를 잡고 free buffer 를 찾아야 한다.
-> latch 를 잡지 못한다면, 'latch : cache buffers lru chain' wait event 발생한다.
#) cache buffers lru chain 갯수 확인
select count(*) from v$latch_children where name = 'cache buffers lru chain';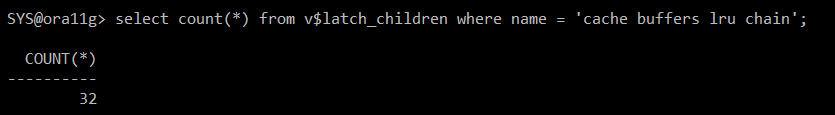
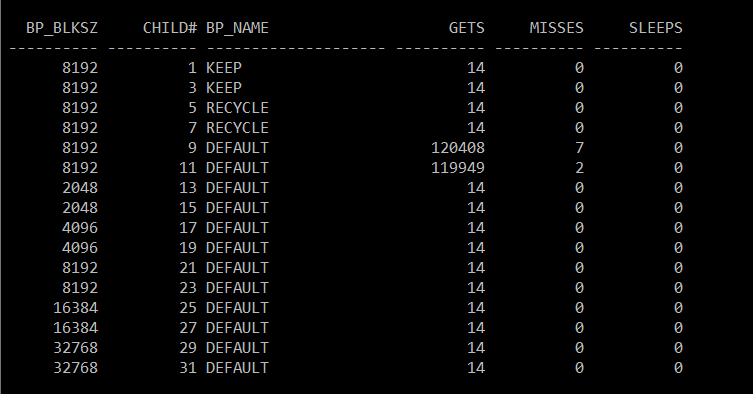
#) 실제 사용하는 latch는 2개!
SELECT A.BP_BLKSZ,
C.CHILD#,
A.BP_NAME,
C.GETS,
C.MISSES,
C.SLEEPS
FROM X$KCBWBPD A, X$KCBWDS B, V$LATCH_CHILDREN C
WHERE B.SET_ID BETWEEN A.BP_LO_SID AND A.BP_HI_SID
AND C.ADDR = B.SET_LATCH
ORDER BY 2; 8192 9 DEFAULT 120408 7 0 ★
8192 11 DEFAULT 119949 2 0 ★
#) buffer cache 관리 과정
1. Latch 획득 및 Free Buffer 탐색
- 세션은 Latch를 획득하고, 먼저 보조 리스트에서 Free Buffer 를 찾는다.
2. 보조 리스트 고려
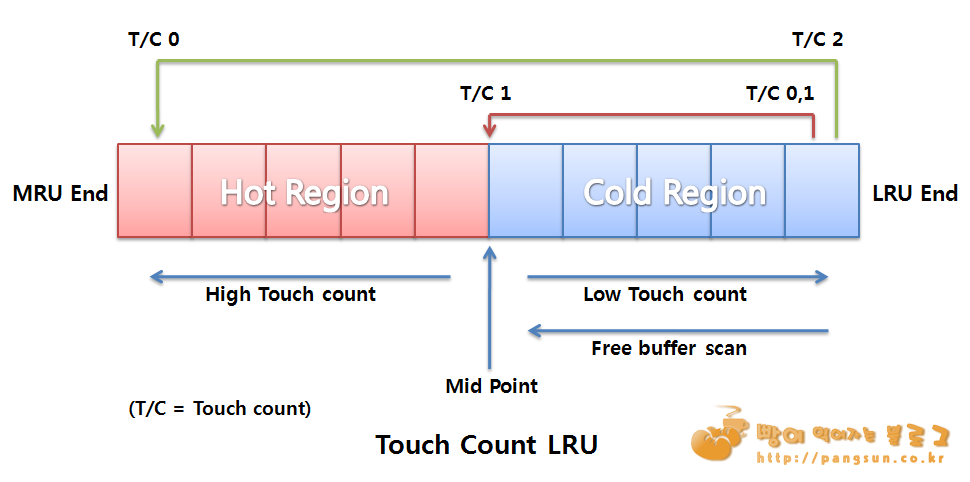
- 보조 리스트의 buffer가 모두 사용된 경우, 메인 리스트의 Cold Region에서부터 스캔하여 Free Buffer 를 찾는다.
- Touch count가 1 이하인 buffer를 발견 → Exclusive Mode 로 Pin하고 해당 Buffer를 사용
- Touch count가 2 이상이 buffer 를 만나면 → Hot Region 의 맨 앞으로 이동하고, Touch count를 0으로 초기화 한다.3. 3. Dirty Buffer 처리
- Free Buffer 를 찾을 때 Dirty Buffer 가 발견되면 LRUW 리스트로 이동한다.
4. Buffer Lock 및 읽기 작업
- Free Buffer를 찾으면 해당 Buffer에 대한 Buffer Lock을 Exclusive Mode 로 획득한다.
- 데이터 파일의 블록을 해당 버퍼로 읽어들인다.
- 다른 세션이 동일한 블록을 조회하려 할 때, Redo by Other Session Wait Event 가 발생할 수 있다.
( 메모리에서 찾았다면 해당 이벤트 발생하지 않는다. )
5. Free Buffer 가 없을 때 대응
- Free Buffer를 찾지 못하면 메모리의 40%를 스캔하고도 Free Buffer를 찾지 못하면 DBWR에게 Dirty Buffer 를 파일에 기록하고 Free Buffer를 확보할 것을 요청한다.
- DBWR 작업 중에 Free Buffer 를 확보할 때까지 Free Buffer Wait Event 가 발생한다. (해석: free buffer 가 없다. )
6. 문제 대응
- Free Buffer 부족이 과하게 발생하면 메모리용량 조절 및 문장 튜닝으로 해결
- 문장 튜닝도 해도 wait event 발생하면? 메모리 사이즈 조절해야 한다.
#) _db_block_max_scan_pct 값 확인
SELECT a.ksppinm Parameter, b.ksppstvl Session_Value, c.ksppstvl Instance_Value
FROM x$ksppi a, x$ksppcv b, x$ksppsv c
WHERE a.indx = b.indx
AND a.indx = c.indx
AND a.ksppinm = '_db_block_max_scan_pct';
#) touch count 2 이상인 buffer 를 만나면 hot region 맨 앞으로(head) 옮김
SELECT a.ksppinm Parameter, b.ksppstvl Session_Value, c.ksppstvl Instance_Value
FROM x$ksppi a, x$ksppcv b, x$ksppsv c
WHERE a.indx = b.indx
AND a.indx = c.indx
AND a.ksppinm = '_db_aging_hot_criteria';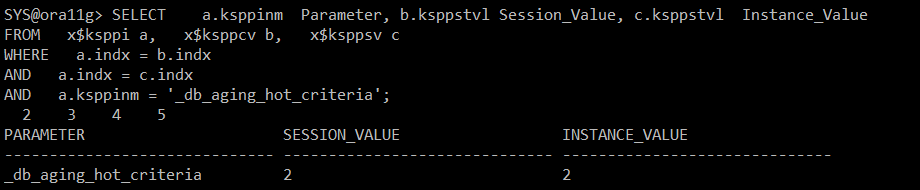
<HR sess_1>
create table cbc_latch(id number, name char(100));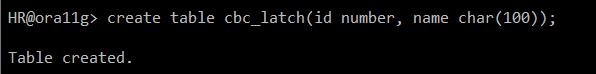
#) 대량의 Data 및 랜덤으로 넣기 + 저장
insert into cbc_latch(id, name) select level, 'oracle'||level
from dual
connect by level <= 500000
order by dbms_random.value;
commit;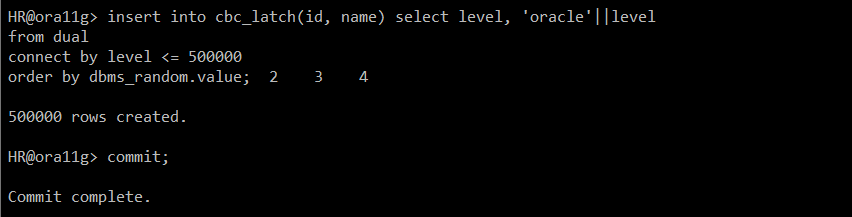
#) NONUNIQUE 생성
create index cbc_latch_idx on cbc_latch(id);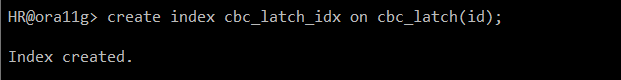
#) 생성 확인
select index_name, uniqueness from user_indexes where index_name = 'CBC_LATCH_IDX';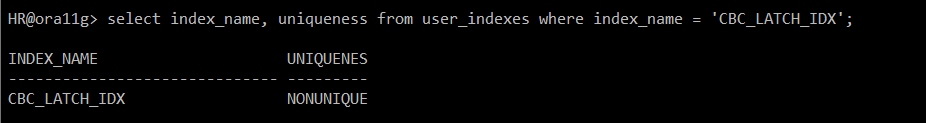
#) sess_1 생성 : HR 계정
exec dbms_application_info.set_client_info('sess_1')
#) sess_2 생성 : HR 계정
exec dbms_application_info.set_client_info('sess_2')
<SYS session_1>
select client_info, sid from v$session where client_info in ('sess_1', 'sess_2');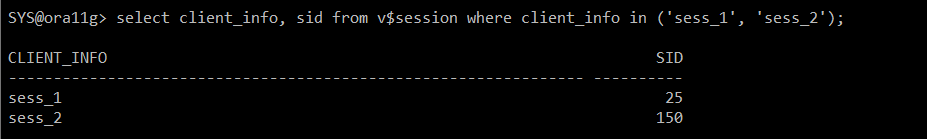
#) shared pool , buffer cache 비워주는 명령어 *2번씩 수행
alter system flush shared_pool;
alter system flush buffer_cache;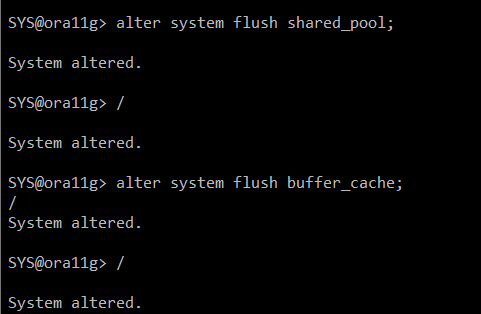
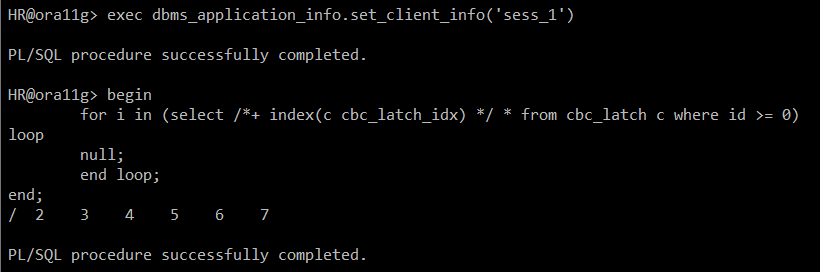
# sess_1, sess_2 동시에 실행! #
#) HR sess_1 생성
begin
for i in (select /*+ index(c cbc_latch_idx) */ * from cbc_latch c where id >= 0)
loop
null;
end loop;
end;
/
#) HR sess_2 생성
begin
for i in (select /*+ index(c cbc_latch_idx) */ * from cbc_latch c where id >= 0)
loop
null;
end loop;
end;
/
<SYS session_1>
#) 대기 이벤트 확인
select sid, event, wait_class, wait_time, seconds_in_wait, state
from v$session_wait
where sid in (25, 150);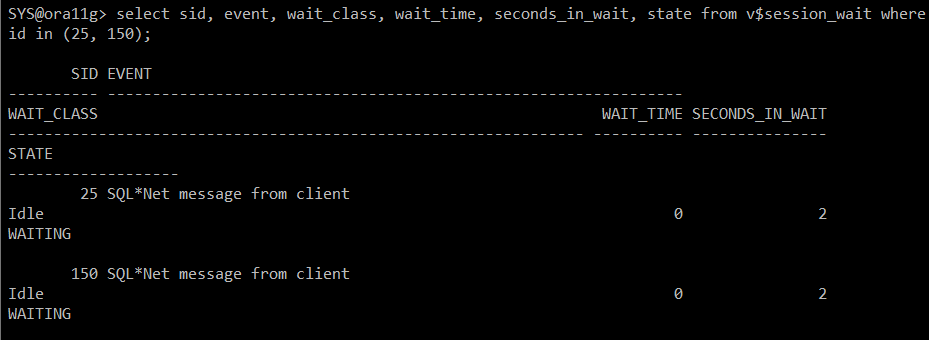
#) sid 확인
select sid, prev_sql_id from v$session where sid in (25, 150);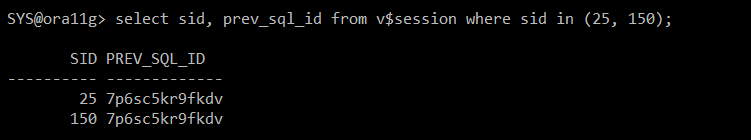
#) 실행 계획 정보 확인
▶ 확인 되지 않음
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor('7p6sc5kr9fkdv',0));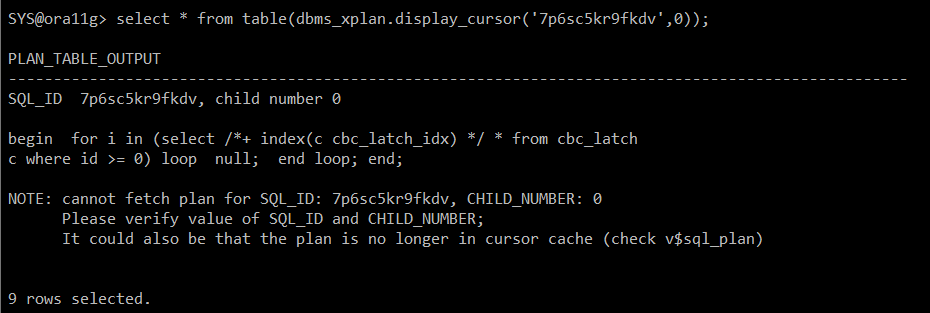
#) 실행 계획 정보 확인
▶ SQL developer 에서 실행계획 확인 가능.
select /*+ index(c cbc_latch_idx) */ * from cbc_latch c where id >= 0;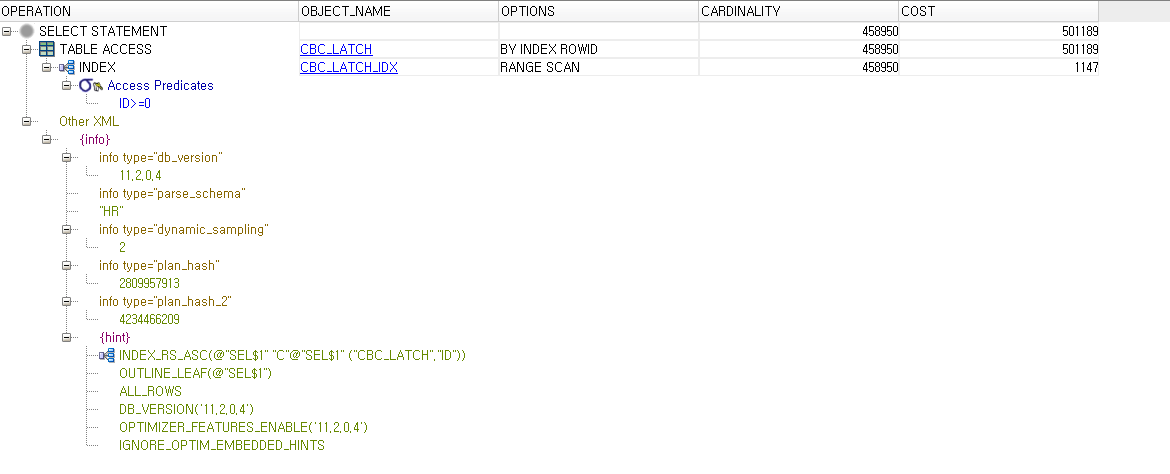
<SYS session_2>
#) 이벤트 확인
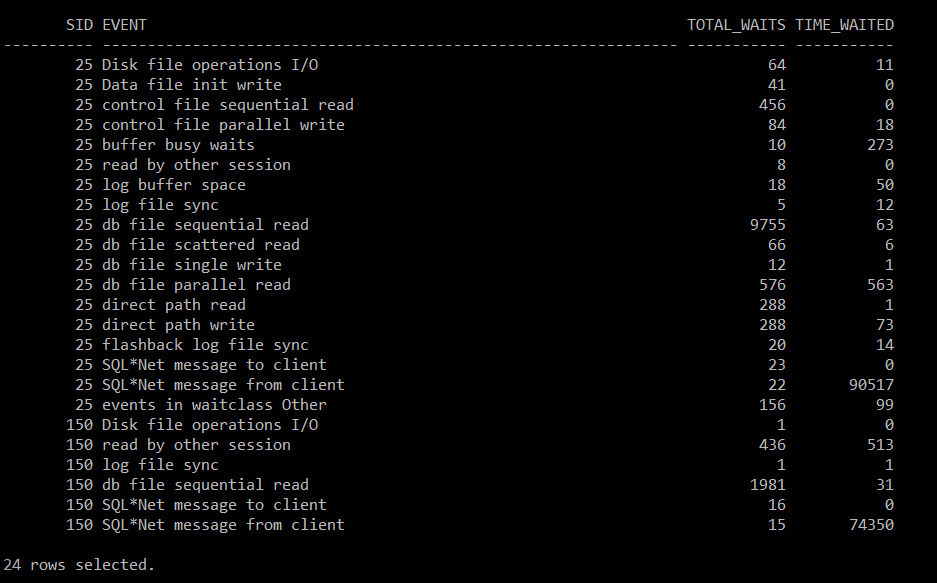
select sid, event, total_waits, time_waited from v$session_event where sid in (25, 150);db file scattered read => index, table full scan
예제2)
<HR sess_1>
#) 기존에 있던 table 삭제
drop table cbc_latch purge;
#) session 생성
exec dbms_application_info.set_client_info('sess_1')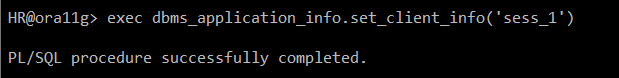
#) table 생성
create table cbc_latch(id number, name char(100));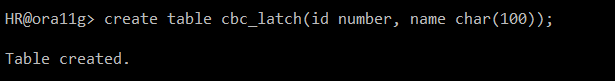
#) data 로드 및 저장
insert into cbc_latch(id, name) select level, 'oracle'||level
from dual
connect by level <= 500000
order by dbms_random.value;
commit;
#) NONUNIQUE 생성
create index cbc_latch_idx on cbc_latch(id);
select index_name, uniqueness from user_indexes where index_name = 'CBC_LATCH_IDX';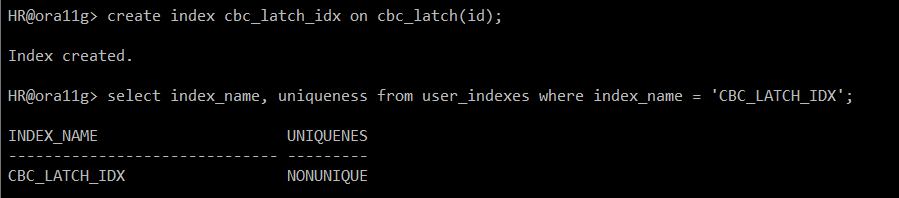
<HR sess_1 >
exec dbms_application_info.set_client_info('sess_1')
<HR sess_2 >
exec dbms_application_info.set_client_info('sess_2')
<SYS sess_1>
alter system flush shared_pool;
alter system flush buffer_cache;
#) HR sess_1, sess_2 확인
select client_info, sid from v$session where client_info in ('sess_1', 'sess_2');
<HR sess_1 >
begin
for i in (select * from cbc_latch c where id >= 0)
loop
null;
end loop;
end;
/
<HR sess_2>
begin
for i in (select * from cbc_latch c where id >= 0)
loop
null;
end loop;
end;
/
<SYS sess_1>
select sid, event, wait_class, wait_time, seconds_in_wait, state
from v$session_wait
where sid in (10, 27);
(sys session_2)
#) session_sid별로 대기 이벤트 확인
select sid, event, total_waits, time_waited from v$session_event where sid in (10, 27); SID EVENT TOTAL_WAITS TIME_WAITED
---------- ---------------------------------------------------------------- ----------- -----------
10 Disk file operations I/O 5 0
10 enq: RO - fast object reuse 2 2
10 log buffer space 42 188
10 log file sync 6 7
10 db file sequential read 8483 210
10 direct path read 288 0
10 direct path write 288 34
10 flashback log file sync 3 4
10 SQL*Net message to client 21 0
10 SQL*Net message from client 20 85586
10 SQL*Net break/reset to client 2 0
10 events in waitclass Other 6 7
27 Disk file operations I/O 1 0
27 log file sync 1 2
27 db file sequential read 92 40
27 SQL*Net message to client 13 0
27 SQL*Net message from client 12 92191
17 rows selected.
#) session별로 prev_sql_id 확인
select sid, prev_sql_id from v$session where sid in (10, 27); SID PREV_SQL_ID
---------- -------------
10 7h8b585us0p6n
27 7h8b585us0p6n
#) 실행 계획 정보 확인
=> 확인 불가
select * from table(dbms_xplan.display_cursor('7h8b585us0p6n',0));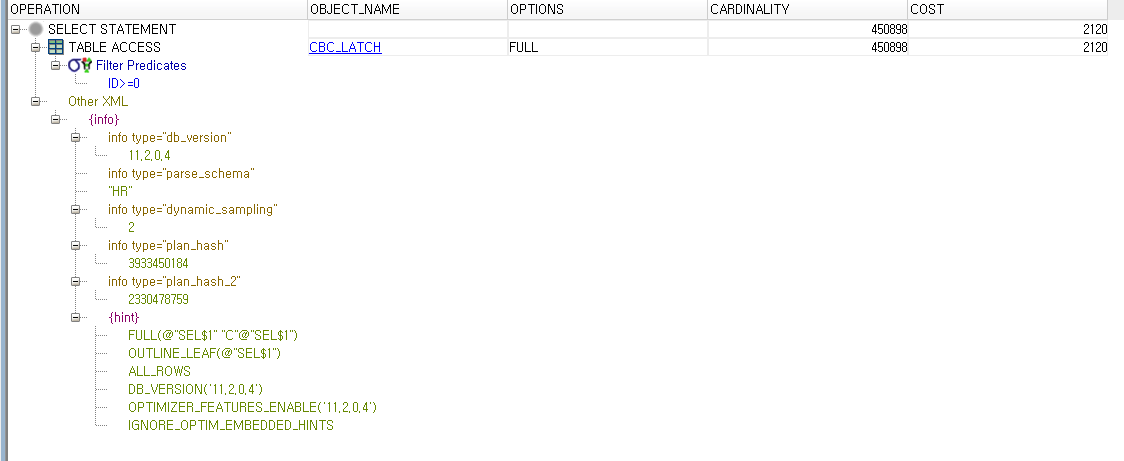
'Data Base > SQL 튜닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Transaction 처리 순서 (1) | 2024.02.07 |
|---|---|
| FLM(FreeList Management) & ASSM(Auto Segment Space Management) (0) | 2024.02.06 |
| Row Cache Lock (0) | 2024.02.05 |
| Version Count_ 바인드 변수 size 설정 (0) | 2024.02.05 |
| Shared Pool Latch, library cache latch (1) | 2024.02.05 |